A magnetic bearing is a new type of high - performance bearing. It is a form of support that uses magnetic forces to bear loads or suspend rotors. Compared with traditional ball bearings, sliding bearings, and oil - film bearings, magnetic bearings have no mechanical contact. The rotor can reach a very high operating speed. They have advantages such as low mechanical wear, low energy consumption, low noise, long life, no need for lubrication, and no oil pollution. They are especially suitable for special environments such as high - speed, vacuum, and ultra - clean conditions.
Magnetic bearings can be widely used in fields such as machining, turbomachinery, aerospace, vacuum technology, and identification and testing of rotor dynamic characteristics. They are recognized as promising new - type bearings.
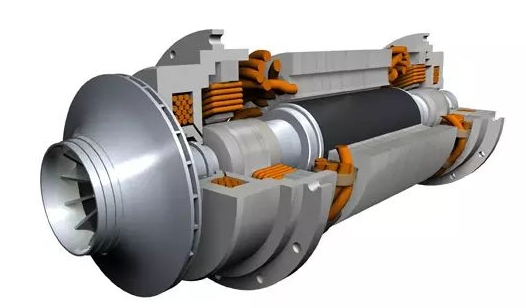
How Does a Magnetic Bearing Work?
Electromagnets are arranged in the form of radial and axial bearings and provide magnetic pull to lift the rotating shaft of the rotating machine. The current in the electromagnets is adjusted by a precise digital control cabinet. The magnetic force is provided to respond to changes in external loads at any time to keep the rotating shaft well - centered. In this way, the rotating shaft is lifted without contact, and the stiffness and damping of the bearing can be adjusted by a digital control cabinet. These features enhance the performance of high - speed rotating machines, making the equipment highly reliable and energy - efficient.
Types of Magnetic Bearings
Magnetic bearings can be classified according to their control methods, sources of magnetic energy, and structural forms. In addition, they can be classified into permanent - type, electromagnet - type, and permanent magnet - electromagnet hybrid - type according to the magnetic field type. They can also be classified into attractive - type and repulsive - type according to the type of bearing suspension force. Superconducting magnetic bearings are further divided into low - temperature superconducting and high - temperature superconducting types.
There are some special restrictions among different types in the above classifications, and special attention should be paid to the following:
① Permanent - magnet - type bearings can only be passive - type, and passive - type bearings cannot be stable in all three directions. At least one direction should adopt an active - type.
② DC - excited - type bearings can only be active - type.
③ Pure electromagnet - type bearings can only be 5 - degree - of - freedom control - type bearings, with relatively large volume, mass, and power consumption.
④ Repulsive - type magnetic bearings are generally rarely used because of their low magnetic force utilization rate and more complex structure compared with attractive - type bearings.
Characteristics of Magnetic Bearings
(1) No Contact, No Wear, No Lubrication
When a magnetic suspension bearing is working, it is in a suspended state. There is no contact between the relatively moving surfaces, so no mechanical friction or contact fatigue occurs. This solves the problems of component wear and replacement in the unit. At the same time, a series of devices such as the lubrication system are omitted, which not only saves space but also eliminates the environmental pollution caused by the aforementioned devices.
(2) Low Vibration, Low Noise, Low Power Consumption
The rotor of a magnetic suspension bearing avoids the large - amplitude vibration and high - decibel noise caused by contact and collision in traditional bearings during operation. This improves stability, reduces maintenance costs, and extends its service life. At the same time, the low power consumption of magnetic suspension bearings is only 6% - 25% of that of traditional mechanical bearings. When the rotational speed is 10,000 r/min, its power consumption is only about 15% of that of mechanical bearings.
(3) High Rotational Speed, High Precision, High Reliability
The rotor is allowed to rotate at a high speed. Its rotational speed is mainly limited by material strength and can operate under super - critical conditions with hundreds of thousands of revolutions per minute. Moreover, the rotational accuracy of the rotor has reached the micron level or even higher, which is far beyond the reach of ordinary mechanical bearings in terms of rotational speed and accuracy. In addition, the reliability of electronic components is much higher than that of traditional mechanical parts.
(4) Controllability, On - line Condition Monitoring, Test and Diagnosis
We can control the static and dynamic performance of magnetic suspension bearings online. In fact, its system itself realizes the integration of condition monitoring, fault diagnosis, and online adjustment.





 Customer service 1
Customer service 1  Customer service 2
Customer service 2